Blog
Dental hygiene tips for healthy teeth & gums
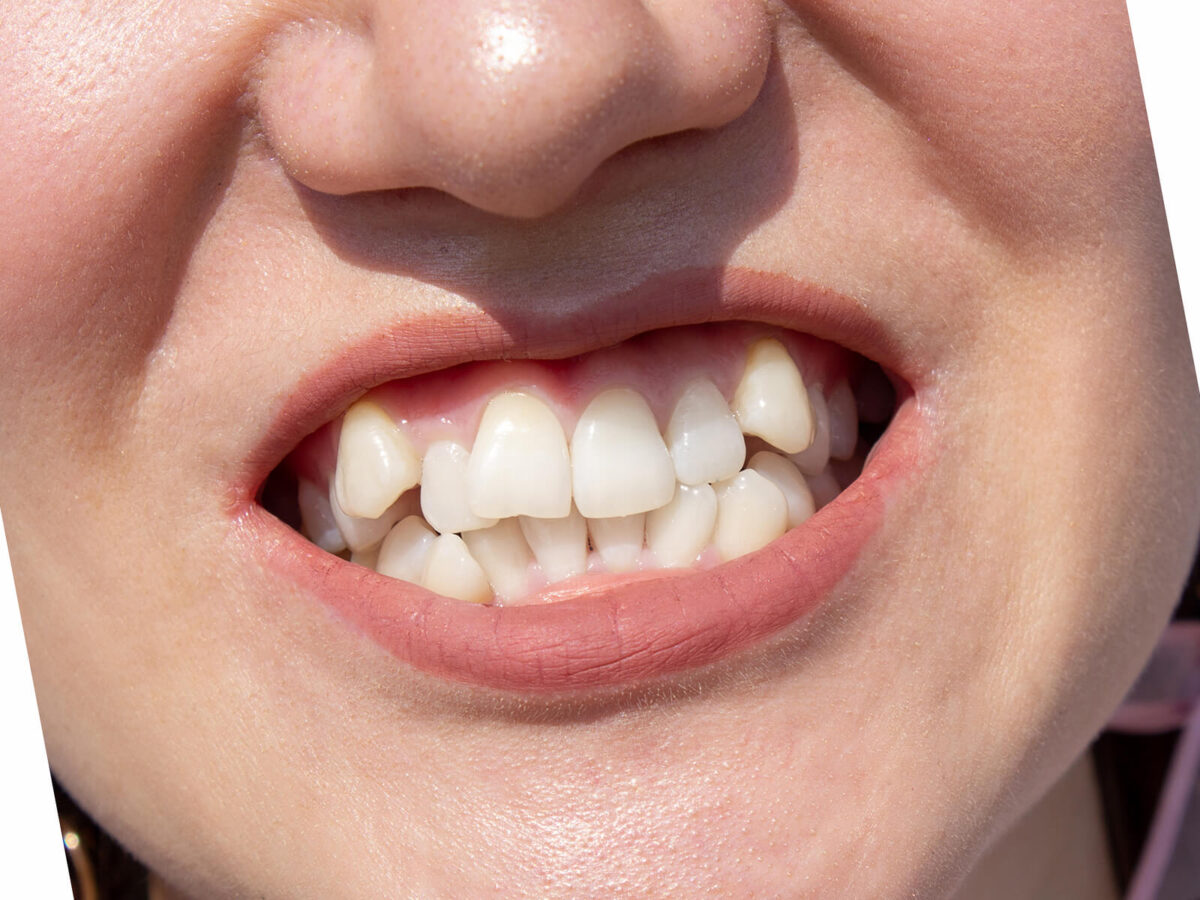
Teeth Shifting: Signs Your Teeth Are Shifting
Teeth shifting is a typical phenomenon that several reasons, including age, oral habits, and orthodontic history can cause. Recognizing the indicators of tooth shifting is critical for maintaining good dental health and avoiding future problems. This article looks at essential symptoms that your teeth may be shifting, such as visible gaps, changes in your bite, and tooth movement.
Some Common Signs Your Teeth Are Shifting
1. Gaps or Spaces:
a. Signs of Shifting: New gaps or spaces between teeth may suggest shifting. Possible causes of teeth shifting include changes in bone structure and the influence of activities such as teeth grinding or tongue thrusting.
b. Diastema: Sign of Shifting: A space between the front two teeth (diastema) can indicate tooth shifting. Diastema can occur due to natural tooth shifting or tooth loss, which allows neighboring teeth to move into the unfilled space.
2. Crowding:
a. Sign of Shifting: Increased crowding, such as tightly packed or overlapping teeth, indicates shifting. Shifting can occur when there is insufficient space in the jaw, causing crowding as teeth seek new locations.
b. Tooth Overlaps Sign of Shifting: Previously aligned teeth may now overlap or twist. Wisdom teeth eruption, dental extractions, and bite alterations can all contribute to tooth overlap.
3. Bite Alignment Changes:
a. An overbite or underbite can suggest shifting teeth. Natural aging, teeth grinding (bruxism), and untreated orthodontic disorders can all cause alterations in bite alignment.
b. Difficulty biting: Difficulty biting or chewing can indicate a shift, especially if it is a novel sensation. Shifting teeth can disrupt the normal alignment of the upper and lower teeth, reducing the ability to bite and eat comfortably.
4. Tooth Mobility:
a. Loose Teeth: Sign of Shifting: The sensation of loose or mobile teeth can indicate shifting. Potential causes of tooth movement include periodontal disease, bone loss, and changes in the surrounding structures.
b. Teeth Movement Upon Touch: Sign of Shifting: If your teeth shift when touched, it indicates instability. Possible causes of tooth movement include periodontal disease, trauma, and changes in the supporting bone.
5. Pain or discomfort:
a. Tooth Sensitivity: Sign of Shifting: Increased tooth sensitivity, particularly to hot or cold temperatures, may indicate shifting teeth. Changes in dental alignment may expose sensitive areas, resulting in increased sensitivity.
b. Signs of moving: Discomfort or pain during chewing, biting, or applying pressure could indicate teeth moving. Shifting teeth can cause unequal pressure distribution while biting, which can be uncomfortable.
6. Impacted Wisdom Teeth:
a. Pain or Swelling at the rear of the Jaw: Sign of Shifting: Pain, swelling, or discomfort in the rear of the jaw, particularly around the wisdom tooth area, may indicate shifting. Wisdom teeth, whether impacted or erupting, can affect the alignment of neighboring teeth.
Conclusion
Early detection of tooth shifting is crucial for effective treatments and prevention. Regular dental check-ups, particularly if you notice these symptoms, are essential for maintaining good oral health. Whether it’s the formation of gaps, changes in bite alignment, or tooth mobility, early detection enables suitable orthodontic or dental interventions to address the root causes. If you see any troubling changes in your teeth, consult your dentist or orthodontist immediately to establish the best course of action for maintaining the health and alignment of your smile.


